Blog
Hip Replacement Surgery
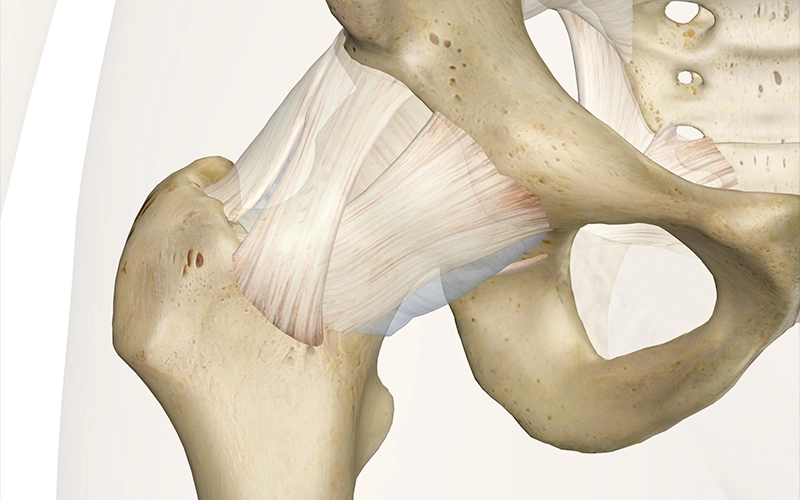
Hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful orthopedic procedures and can significantly reduce pain while improving a patient’s quality of life. Proper preparation before surgery and careful adherence to postoperative instructions play a vital role in achieving a successful outcome and a faster return to daily activities.
Preparing Your Home: Setting Up a Recovery Station
Before undergoing hip replacement surgery, it is recommended to prepare a recovery station at home. Place commonly used items such as a telephone, television remote control, radio, tissues, trash bin, drinking cup, and other daily necessities close to the area where you will spend most of your time after surgery. This setup minimizes unnecessary movement, bending, or reaching during the recovery period.
Preoperative Preparation
Once the decision for hip replacement surgery is made, planning ahead can greatly support your recovery:
-
Insurance Coverage: If you have health insurance, ensure that your coverage is valid and understand its benefits.
-
Dental Procedures: All dental treatments should be completed before surgery to reduce the risk of postoperative infection.
-
Blood Donation: In some cases, your physician may recommend storing your own blood at the hospital several weeks before surgery.
-
Preoperative Medical Evaluation: Approximately two weeks before hospitalization, medical assessments such as blood and urine tests will be performed. You may also undergo an electrocardiogram (ECG) and chest X-ray. The orthopedic surgeon may consult with other physicians to confirm that your overall health is suitable for surgery.
Planning for Recovery
Arrange transportation from the hospital to your home in advance. During the first few weeks after surgery, ask family members or friends to stay with you and assist with household tasks. Prepare meals ahead of time, especially foods that are easy to cook. Secure loose rugs and electrical cords, install a raised toilet seat if possible, and place frequently used items within easy reach so that bending or pulling is unnecessary.
Overview of Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery is considered one of the most successful surgical procedures. Most artificial hip joints last at least 15 to 20 years, and on average, fewer than 10 percent of patients require revision or corrective surgery.
Anesthesia Options
Hip replacement surgery is a major procedure and requires either general anesthesia or regional anesthesia such as spinal or epidural anesthesia. With general anesthesia, the patient is fully asleep during the procedure. With spinal or epidural anesthesia, the patient remains awake but does not feel pain. The type of anesthesia is selected in consultation with an anesthesiologist based on the patient’s medical condition. Advances in anesthesia medications and monitoring equipment have made anesthesia safer than in the past.
The Surgical Procedure
You will be instructed not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the night before surgery. Upon admission to the hospital, your vital signs—blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and body temperature—will be assessed, and medications may be given to help you relax. The surgery typically lasts between two and four hours.
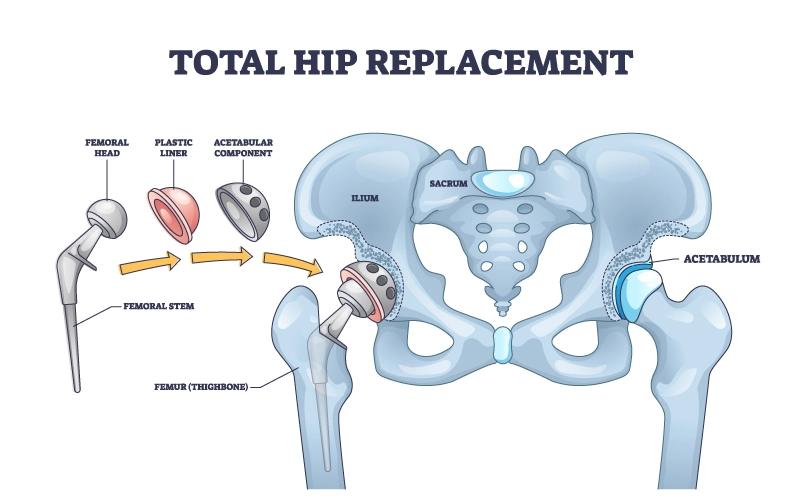
The orthopedic surgeon makes an incision to expose the hip joint. The damaged portions of the femur and hip socket are carefully removed to create space for the new joint. A metal cup with a plastic liner is placed into the hip socket, and a metal stem with a ball is inserted into the femur to form the new hip joint.
Types of Hip Implants

-
Cemented Implants: A special bone cement is used to secure the artificial joint in place. Patients may often bear weight on the new hip almost immediately.
-
Cementless Implants: The bone gradually grows around the implant, securing it naturally. Your physician will inform you when full weight-bearing is allowed. Some movements may be restricted for up to three months.
-
Hybrid Implants: One component is cemented while the other is fixed without cement.
The orthopedic surgeon determines the most suitable implant type based on age, bone quality, and lifestyle.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation begins immediately after hip replacement surgery. The main goals include increasing muscle strength, improving hip joint mobility, protecting the new joint, and returning to normal daily activities.
In most cases, a physical therapist will help you sit, stand, and begin walking as early as the day after surgery. You will be taught exercises to restore joint motion, strength, and independence. Most of the hip’s range of motion returns within the first few weeks. Failure to follow the exercise program may result in stiffness around the joint and long-term limitation. Continuing exercises after hospital discharge is highly beneficial, and hospital staff can assist in arranging physical therapy sessions.
Recovery at Home
Recovery at home begins even before leaving the hospital. Before discharge, make sure you understand how to take your medications, when dressings and stitches should be removed, and the schedule for follow-up visits.
Preventing Complications at Home
-
Infection: The most common cause of infection after hip replacement is bacteria entering the bloodstream. Dental procedures, urinary tract infections, and skin infections can introduce bacteria that may settle around the artificial joint. Antibiotics should be taken before dental or surgical procedures that may cause bacteremia.
-
Blood Clots: To reduce the risk of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism—most common in the first weeks after surgery—follow your physician’s instructions carefully. Warning signs include increased pain, redness, tenderness, or swelling in the calf, ankle, or foot.
-
Pulmonary Embolism Warning Signs: Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or chest pain associated with coughing require immediate medical attention.
-
Loosening of the Implant: Some artificial joints may loosen over time where the metal or cement meets the bone. A loose implant can cause pain and may require revision surgery if symptoms become severe.
-
Dislocation: In rare cases, the hip joint may dislocate after surgery. Avoid bending forward, crossing your legs, or rotating the operated leg inward until the muscles, tendons, and ligaments have healed. When sitting in a car, sit on a firm cushion and keep the operated leg extended.
Your Role in a Successful Outcome
Set personal goals and actively work toward achieving them. Consistent physical therapy and adherence to an exercise program play a crucial role in a successful recovery. Each exercise session is a step toward regaining independence and returning to an active lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long will I stay in the hospital?
The average hospital stay after hip replacement surgery is approximately 3 to 5 days.
How long does recovery take?
Recovery varies from person to person. Most patients use a walker or crutches initially and gradually increase activity. Many are able to resume most normal activities within a few weeks.
Will I need a blood transfusion?
Approximately half of patients do not require a blood transfusion. Some patients may store their own blood before surgery if advised by their physician.
How successful is hip replacement surgery?
Hip replacement surgery is one of the most effective orthopedic procedures, and many patients never require revision surgery.
How long does an artificial hip joint last?
Like any mechanical device, an artificial hip joint may wear out over time. However, in many cases, one hip replacement lasts a lifetime. If needed, revision surgery can be performed more than once.