Blog
Appropriate Treatment Methods for Orthopedic Patients
The treatment methods for orthopedic patients depend on the specific condition, type of injury or disease, and the severity of the issue. Below is a general categorization of these treatment methods:
1. Non-Surgical (Conservative) Treatments
These treatments are typically the first line of defense for orthopedic patients, especially when the problem is not too severe:
-
Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises to improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and increase muscle strength.
-
Medication: The use of anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, or supplements such as glucosamine to reduce pain and inflammation.
-
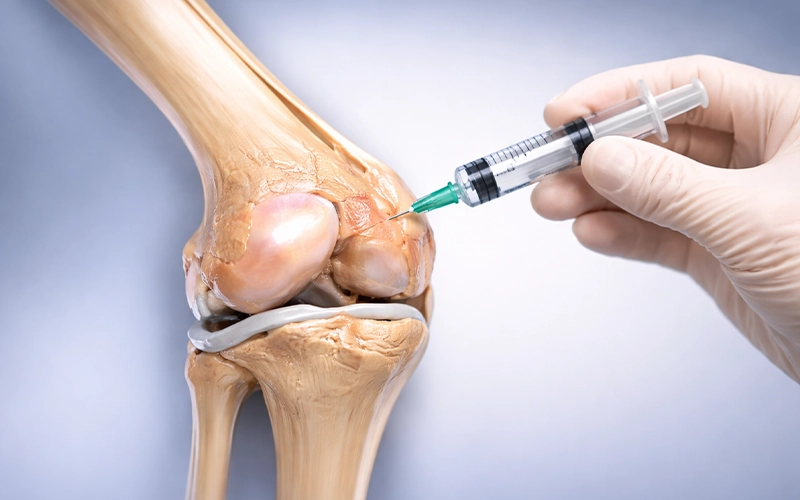
Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections into the joint to reduce inflammation and improve joint movement.
-
Braces or Splints: Supportive devices used to reduce pressure on the joints and provide additional stability.
2. Surgical Treatments
If non-surgical treatments are not effective and the damage is severe, surgery might be necessary. These treatments are generally used when joint or bone problems are more advanced:
-
Joint Replacement: In cases of severe joint damage (such as advanced osteoarthritis), total joint replacement surgery is performed. This is common in knee, hip, and shoulder joints.
-
Ligament Repair or Reconstruction: Surgery to repair or reconstruct ligaments, especially in cases of cruciate ligament injuries or other key ligaments in the body.
-
Bone Corrective Surgery: Procedures to correct deformities in bones or joints, such as osteotomy (surgery to change the angle or position of bones).
-
Fusion (Fusion Surgery): The fusion of two bones to provide additional stability, typically performed in the spine.
-
Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat internal joint problems. This involves the use of a small camera (arthroscope) to examine and treat joint issues.
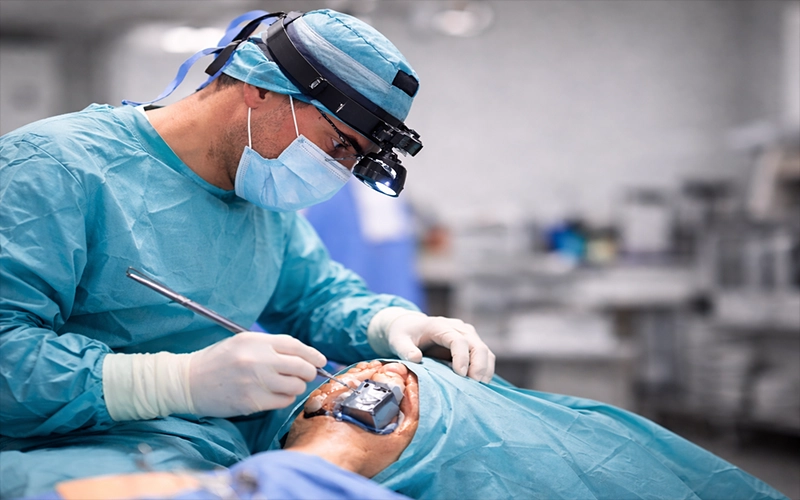
3. Rehabilitation Techniques
Rehabilitation is crucial for recovery after both surgical and non-surgical treatments. These techniques help accelerate healing, restore function, and prevent further damage:
-
Hydrotherapy (Water Therapy): Exercises performed in water that reduce pressure on the joints while promoting movement. This is especially helpful for patients who are in significant pain and need a low-impact way to perform strengthening exercises.
-
Massage Therapy: Used to reduce muscle tension, improve blood circulation, and relieve pain in affected areas.
-
Exercise Programs: Specialized exercises designed to strengthen joints and prevent re-injury. These programs include both strengthening and stretching exercises that gradually build muscle strength and restore normal function.
4. Lifestyle Modifications and Prevention
Lifestyle adjustments and preventive measures are essential for maintaining joint health and preventing future injuries:
-
Weight Management: Reducing excess weight can decrease the pressure on joints, particularly the knees and hips. This helps prevent further damage and reduces pain.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Educating patients on how to prevent physical injuries and improve joint health through appropriate exercise, posture, and movement techniques.
Conclusion:
Treatment methods for orthopedic patients vary depending on the type and severity of the problem. Non-surgical treatments, surgical procedures, rehabilitation programs, and lifestyle modifications all play an important role in improving joint function, reducing pain, and speeding up recovery. Collaboration between the patient and healthcare team, along with adherence to the prescribed treatment plan, is key to achieving the best results and maintaining an active, pain-free lifestyle.